(Saturday, February 7, 2026, 20:30~21:00)
https://biosciencedbc.jp/news/20260204-01.html
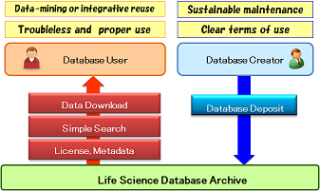
If a database is inadequate in terms of its description, unclear with respect to the terms of use, or is not downloadable, it may not be fully used, cited or rightly acknowledged by the (research) communities. This is even true for databases with high-quality datasets.
The Life Science Database Archive maintains and stores the datasets generated by life scientists in Japan in a long-term and stable state as national public goods. The Archive makes it easier for many people to search datasets by metadata (description of datasets) in a unified format, and to access and download the datasets with clear terms of use (see here for detailed descriptions).
In addition, the Archive provides datasets in forms friendly to different types of users in public and private institutions, and thereby supports further contribution of each research to life science.
| Database name⇅ | Maintenance site⇅ | Principal creator⇅ | Database classification⇅ | Organism⇅ | Summary⇅ | License⇅ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIKENopen_in_new | Shuichi Onami | Dynamic database | mouse, zebrafish, fruit fly, nematode, E. coli |
The database of collecting and sharing quantitative data of biological dynamics , which are generated from experimental measurement or computer simulation. |
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Department of Drug Discovery Medicine, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicineopen_in_new | Shinya Oki | Expression | human, mouse, fruit fly, nematode, budding yeast, rat |
The database of the result of analysis processed from the entire ChIP-Seq data archived in Sequence Read Archive. |
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Kazusa DNA Research Instituteopen_in_new | Nozomu Sakurai | Experimental Metadata (Materials and Methods) | whole organism |
A database specified for managing information on experimental methods (metadata) which is accompanied with the experimental data obtained from metabolomics studies.
|
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| The Targeted Proteins Research Programopen_in_new | Hideki Taguchi | Protein properties | E. coli |
Database of solubilities of all E.coli proteins translated by using an in vitro translation system, and of chaperone effects on their aggregation. |
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| National Institute of Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tokyo Waterfrontopen_in_new | Chie Motono | Protein structure, Human ORFs, Protein sequence | human |
SAHG is a comprehensive database of predicted structures of all human proteins.
|
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Database name⇅ | Maintenance site⇅ | Principal creator⇅ | Database classification⇅ | Organism⇅ | Summary⇅ | License⇅ |






