(Saturday, February 7, 2026, 20:30~21:00)
https://biosciencedbc.jp/news/20260204-01.html
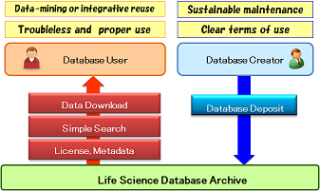
If a database is inadequate in terms of its description, unclear with respect to the terms of use, or is not downloadable, it may not be fully used, cited or rightly acknowledged by the (research) communities. This is even true for databases with high-quality datasets.
The Life Science Database Archive maintains and stores the datasets generated by life scientists in Japan in a long-term and stable state as national public goods. The Archive makes it easier for many people to search datasets by metadata (description of datasets) in a unified format, and to access and download the datasets with clear terms of use (see here for detailed descriptions).
In addition, the Archive provides datasets in forms friendly to different types of users in public and private institutions, and thereby supports further contribution of each research to life science.
| Database name⇅ | Maintenance site⇅ | Principal creator⇅ | Database classification⇅ | Organism⇅ | Summary⇅ | License⇅ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National Institute of Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Tokyo Waterfrontopen_in_new | Toutai Mituyama | RNA sequences | 32,978 species |
The database that hosts a large collection of non-coding transcripts including annotated/non-annotated sequences.
|
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Kazusa DNA Research Instituteopen_in_new | Hisashi Koga | Proteomics | mouse |
The database consists of InGaP and InCeP. InGap is the analysis of 274 mKIAA genes' expressions based on antibody preparation. InCep is the analysis of 50 mKIAA proteins' interactions.
|
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| National Institute of Agrobiological Sciencesopen_in_new | Setsuko Komatsu | Proteome | Rice |
The information on proteins identified from several organs and organelles of rice on two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2D-PAGE) reference maps.
|
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Institute of Medical Science, University of Tokyoopen_in_new | - | Polymorphism | human |
A database of about 197,000 polymorphisms in Japanese population, with annotations such as genes, positions, amino acid substitutions |
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| National Institute of Agrobiological Sciencesopen_in_new | Shoshi Kikuchi | Plant databases - Rice, Microarray, Gene Expression | Rice |
RED II INAHO is the database that analyzed the gene expression of rice using a 60-mer oligonucleotide microarray.
|
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Database name⇅ | Maintenance site⇅ | Principal creator⇅ | Database classification⇅ | Organism⇅ | Summary⇅ | License⇅ |






