(Saturday, February 7, 2026, 20:30~21:00)
https://biosciencedbc.jp/news/20260204-01.html
If a database is inadequate in terms of its description, unclear with respect to the terms of use, or is not downloadable, it may not be fully used, cited or rightly acknowledged by the (research) communities. This is even true for databases with high-quality datasets.
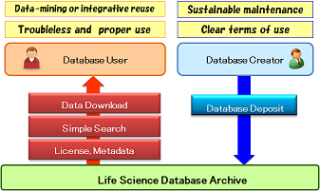
The Life Science Database Archive maintains and stores the datasets generated by life scientists in Japan in a long-term and stable state as national public goods. The Archive makes it easier for many people to search datasets by metadata (description of datasets) in a unified format, and to access and download the datasets with clear terms of use (see here for detailed descriptions).
In addition, the Archive provides datasets in forms friendly to different types of users in public and private institutions, and thereby supports further contribution of each research to life science.
| Database name⇅ | Maintenance site⇅ | Principal creator⇅ | Database classification⇅ | Organism⇅ | Summary⇅ | License⇅ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The University of Tokyoopen_in_new | Takashi Ito | cDNA | budding yeast |
The database of budding yeast 5'cDNA full length clones. |
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| The University of Tokyoopen_in_new | Takashi Ito | Protein-protein interactions | budding yeast |
The database of budding yeast protein-protein interactions obtained from Y2H. |
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| The University of Tokyoopen_in_new | Satoru Miyano | Metabolic and Signaling Pathways | mammals |
The database of pathways associated with differentiation and activation of macrophage.
|
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Database Center for Life Scienceopen_in_new | Kousaku Okubo | Dictionary | 9 species (human, mouse, rat, zebrafish, fruit fly, nematode, budding yeast, fission yeast, Bacillus subtilis) |
Gene names and gene family names were collected for 9 different organisms (including human, mouse, rat, zebrafish, fruit fly, nematode, budding yeast, fission yeast, Bacillus subtilis), and associated with parallel relationship (synonym) and hierarchical relationship (family name). Acronym notations and IDs of typical gene/genome databases are also treated as names. |
CC BY-SA Detail |
|
| Database name⇅ | Maintenance site⇅ | Principal creator⇅ | Database classification⇅ | Organism⇅ | Summary⇅ | License⇅ |